Upcoming NERC system maintenance and upgrade - Tuesday, Feb 10, 2026 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM
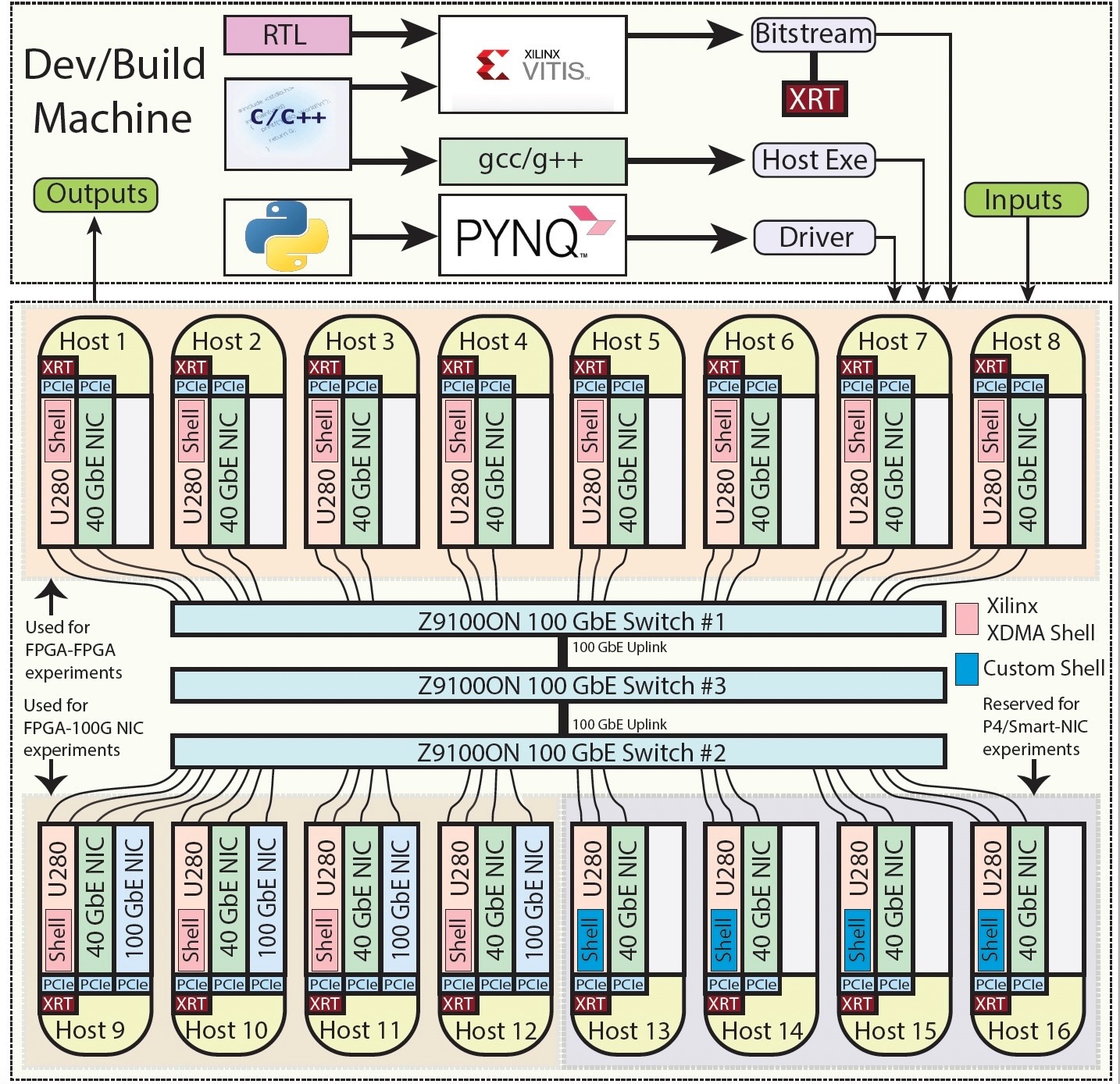
The Open Cloud Testbed (OCT) is a research infrastructure project funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) aimed at exploring new cloud technologies. It provides researchers with cutting-edge hardware, specifically bare-metal servers equipped with FPGA accelerators, to conduct experiments in high-performance computing such as machine learning and AI, scientific computing, and real time monitoring. The FPGA cluster in OCT is located at the Massachusetts Green High Performance Computing Center (MGHPCC) and is part of the CloudLab framework, a research infrastructure initiative designed to provide researchers with flexible, customizable, and scalable cloud computing resources for experimentation. The cluster currently consists of 16 AMD Alveo Accelerator cards which are all directly connected to a 100 Gb/s network. This setup offers researchers and developers low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity, enabling them to exchange data, share resources, and collaborate with peers who use similar FPGA-accelerated computing infrastructures deployed in other clusters or testbeds, whether domestic or international. As of March 2024, we are in the process of enhancing OCT to better support the machine learning community by integrating Versal VCK5000s and Alveo V70s. These devices come with AI engines allowing for applications of different levels of complexities, making them valuable assets within OCT.
The OCT workflow consists of two parts: Development and Deployment. We provide a comprehensive toolchain for users who work on developing applications that are executed on the FPGAs within OCT. The development tools are hosted on VMs within the New England Research Cloud (NERC). Users can remotely access these VMs and build host executables, FPGA bitstreams, and drivers, using the tools that we have provided. Additionally, licenses required for certain intellectual property (IP) cores are also hosted on a dedicated VM. After creating bitstreams and host executables/drivers, users transfer them to the deployment machine(s) on CloudLab, where the FPGAs are installed. After this, they program the FPGAs, execute the host executables, and optionally retrieve the results back to the development machine on NERC.
NERC provides the OpenStack compute infrastructure that is required to create virtual machines to OCT users for building their FPGA projects. These VMs serve as the primary environment for users to design, simulate, verify, and test FPGA configurations and applications. The tools we use in OCT typically demand substantial resources, including several hundred gigabytes of disk space, to accommodate the complexities involved in development workflows. NERC's infrastructure provides the necessary computational power and storage capabilities to host these tools within a cloud environment. Currently, we support our users through two distinct toolflows: the general workflow, providing Xilinx Vitis for general FPGA users, and the custom/P4 workflow, offering Vivado and P4 toolchains tailored specifically for P4/SmartNIC-based projects. With access to all these tools, users can explore different avenues for improving FPGA performance in cloud computing applications.